Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on papular eczema. This article delves into the symptoms and signs of this skin condition, helping you understand what it is, how it manifests, and the best ways to manage it. Whether you’re a patient, a caregiver, or just curious, this guide aims to provide valuable insights.
What is Papular Eczema?
Definition and Overview
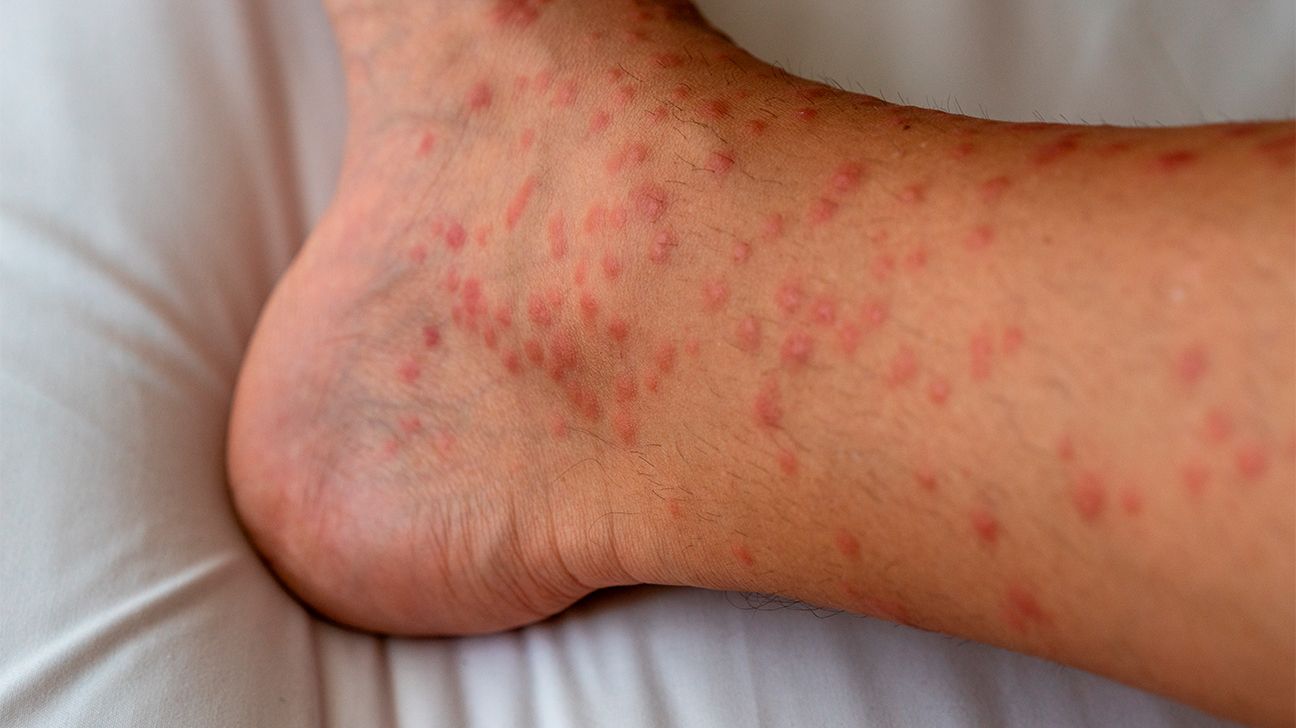
Papular eczema, also known as papular dermatitis, is a type of eczema characterized by small, raised bumps on the skin. These bumps, or papules, are often red and itchy, making the condition uncomfortable and sometimes painful. Unlike other forms of eczema, papular eczema’s hallmark is these distinct papules.
Differences from Other Eczema Types
Unlike atopic dermatitis, which presents as patches of dry, scaly skin, papular eczema primarily features these small, inflamed bumps. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Papular Eczema
Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in developing papular eczema. If you have a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever, you’re more likely to develop this condition. Researchers believe that specific genes make your skin more prone to inflammation.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors like allergens, irritants, and even stress can trigger papular eczema. Common culprits include pet dander, pollen, harsh soaps, and certain fabrics. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Papular Eczema
Early Signs
The early signs of papular eczema can be subtle, often starting with mild itching and small bumps. These symptoms can escalate if not addressed promptly.
Advanced Symptoms
As the condition progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced. Let’s explore these advanced signs in more detail:
Redness and Swelling
The affected areas often become red and swollen, indicating inflammation. This redness can be persistent and spread to surrounding areas.
Itchiness and Irritation
One of the most bothersome symptoms is intense itchiness. Scratching can worsen the condition, leading to more severe irritation and potential infection.
Papules and Lesions
The defining feature of papular eczema is the appearance of papules. These are small, raised bumps that can cluster together, forming lesions. They can be sore and lead to scarring if scratched excessively.
Diagnosing Papular Eczema
Medical History
A thorough medical history is the first step in diagnosing papular eczema. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, family history, and potential exposure to allergens or irritants.
Physical Examination
A physical exam helps identify the characteristic papules and assess the extent of the condition. Your doctor will look for specific patterns and severity of the lesions.
Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, additional tests like skin biopsies or allergy tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Topical Treatments
Topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itchiness. Other options include calcineurin inhibitors and moisturizing cream to maintain skin hydration.
Systemic Treatments
For severe cases, systemic treatments such as oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be recommended. These are usually short-term solutions due to potential side effects.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Simple home remedies like cool compresses, oatmeal baths, and gentle skincare routines can provide relief. Lifestyle changes, including stress management and dietary adjustments, also play a vital role in managing symptoms.
Managing and Preventing Flare-Ups
Skincare Routine
Maintaining a gentle skincare routine is essential for preventing flare-ups. Use mild, fragrance-free products and moisturize regularly to keep your skin barrier intact.
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial. Keep a diary to track flare-ups and potential causes, allowing you to make informed decisions about your environment and lifestyle.
Impact on Quality of Life
Physical Health
Papular eczema can significantly affect physical health, causing discomfort and sleep disturbances. Persistent itchiness and lesions can lead to secondary infections.
Mental and Emotional Well-being
The condition can also impact mental health, leading to stress, anxiety, and depression. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is vital for emotional well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding papular eczema is the first step towards managing it effectively. By recognizing the symptoms and signs, seeking appropriate treatment, and making lifestyle adjustments, you can significantly improve your quality of life. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and with the right strategies, you can manage this condition effectively.
FAQs
- What triggers papular eczema flare-ups?
Common triggers include allergens, stress, harsh soaps, and certain fabrics. Keeping a diary can help identify personal triggers.
- Can papular eczema be cured?
There’s no cure for papular eczema, but with proper management, you can control the symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Are there any natural remedies for papular eczema?
Yes, natural remedies like oatmeal baths, coconut oil, and aloe vera can help soothe the skin and reduce inflammation.
- How is papular eczema different from other types of eczema?
Papular eczema is characterized by small, raised bumps, unlike other types that may present as dry, scaly patches.
- Is papular eczema contagious?
No, papular eczema is not contagious. It’s a chronic skin condition often influenced by genetic and environmental factors.