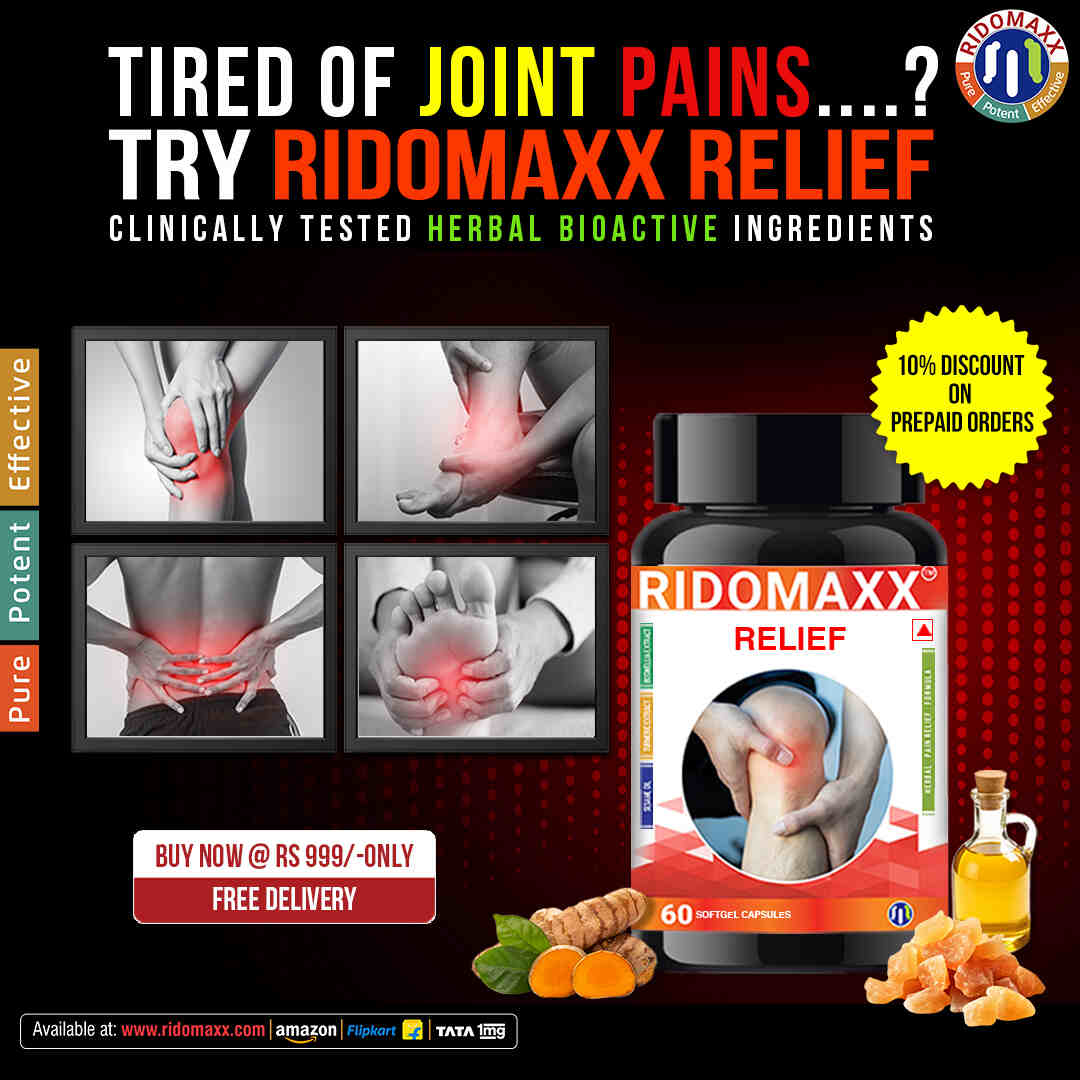
Understanding the various types of pain relief tablets available is essential for effectively managing pain and improving overall quality of life. Pain can stem from numerous sources, including injuries, chronic conditions, or temporary ailments, and the right medication can make a significant difference in how one experiences and copes with discomfort. Each category of pain relief medication, from acetaminophen to opioids, works through different mechanisms, targeting specific types of pain. By familiarizing oneself with these medications, individuals can make informed decisions about their pain management options.
In India, several over-the-counter and prescription pain relief medications are widely available, making it easier for individuals to find suitable options. Among these, the Pain Relief Tablets cater to a variety of needs, whether for mild headaches or more severe pain associated with conditions like arthritis. Understanding these options not only helps in choosing the right medication but also ensures safe and effective pain management tailored to individual requirements.

Here are some Understanding Different Types of Pain Relief Tablets and Their Benefits
1. Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen, also known as paracetamol, is a common and widely used pain reliever and fever reducer. It’s available OTC and is generally considered safe when taken as directed. Acetaminophen works by blocking the production of prostaglandins in the brain. Prostaglandins are hormone-like substances that cause inflammation, pain, and fever. By targeting these pathways, acetaminophen effectively reduces mild to moderate pain and lowers fever without having significant anti-inflammatory properties, making it ideal for headaches, muscle aches, and minor pain relief.
However, it is crucial to use acetaminophen carefully, as overdosing can be dangerous, particularly to the liver. The liver processes acetaminophen, and excessive use can lead to liver damage or even failure. This risk is why it’s essential to adhere to recommended dosages, avoiding multiple medications containing acetaminophen simultaneously, as accidental overdose can easily occur. When taken responsibly, acetaminophen is a safe option for managing everyday pain and discomfort.
2. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs, including ibuprofen, naproxen, and diclofenac, are pain-relieving medications with additional anti-inflammatory and fever-reducing properties. These medications are commonly used for various types of pain associated with inflammation, such as muscle strains, joint pain, and mild arthritis. NSAIDs work by reducing the production of prostaglandins throughout the body. Unlike acetaminophen, NSAIDs address inflammation directly, making them more effective for conditions where inflammation is a primary cause of discomfort.
While NSAIDs are effective, long-term or regular use can pose certain health risks. For instance, taking NSAIDs over an extended period increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, stomach ulcers, and gastrointestinal bleeding. To reduce these risks, doctors often recommend using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary. NSAIDs are generally safe for occasional use but should be used with caution, especially in individuals with a history of cardiovascular or gastrointestinal issues.
3. COX-2 Inhibitors
COX-2 inhibitors are a subclass of NSAIDs designed to provide similar pain and anti-inflammatory relief without the associated gastrointestinal risks. These drugs target the COX-2 enzyme, which plays a significant role in pain and inflammation, while sparing the COX-1 enzyme that helps protect the stomach lining. Celecoxib is one of the most common COX-2 inhibitors available.
COX-2 inhibitors are beneficial for individuals who cannot tolerate traditional NSAIDs or are at higher risk of developing stomach ulcers or bleeding. However, like NSAIDs, they can still carry cardiovascular risks, so they must be used under medical supervision, especially by those with existing heart conditions. For individuals with chronic pain conditions like arthritis, COX-2 inhibitors offer a more stomach-friendly alternative to manage pain effectively.
4. Opioids
Opioids are a potent class of pain relief medications used to manage moderate to severe pain, particularly for short-term pain after surgery or injury or for chronic pain that other medications cannot control. Examples of opioids include codeine, morphine, oxycodone, and co-codamol. Opioids work by binding to receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking the perception of pain and producing a sense of euphoria.
Because opioids are highly effective, they are often prescribed for severe pain; however, they come with significant risks, including dependency and addiction. Due to these risks, opioids are generally reserved for situations where other pain relief methods have proven ineffective. In many cases, physicians also limit the duration and dosage of opioid use and monitor patients closely to avoid potential misuse. Opioids are typically available only by prescription, and their use is regulated to ensure safety and prevent abuse.
5. Adjuvants
Adjuvant medications are drugs not primarily designed for pain relief but have pain-relieving properties, particularly for nerve pain (neuropathic pain). Common adjuvants include gabapentin, amitriptyline, and duloxetine. These medications work on the nervous system, altering the way the brain and nerves perceive and respond to pain signals. For individuals experiencing nerve pain due to conditions like diabetes, shingles, or sciatica, adjuvants offer a targeted approach to pain management.
Adjuvants are often used in conjunction with other pain relief medications to enhance overall pain management, especially when traditional pain relievers are not effective against nerve pain. Because they affect the nervous system, adjuvants may come with side effects, such as drowsiness or dizziness, and their use typically requires a doctor’s guidance.
6. Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, commonly referred to as steroids, are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that relieve pain by reducing inflammation in the body. Examples include hydrocortisone, methylprednisolone, prednisone, and prednisone. Corticosteroids mimic cortisol, a hormone naturally produced by the adrenal glands, and are often used to treat inflammatory conditions like arthritis, allergies, and autoimmune disorders.
While corticosteroids can provide significant relief, especially for inflammation-related pain, they are generally not recommended for long-term use due to potential side effects, such as weight gain, high blood pressure, and weakened immune function. Physicians may prescribe corticosteroids for short-term use during flare-ups of inflammatory conditions or in low doses for chronic conditions. Steroids are typically available by prescription, and doctors often monitor their use closely.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of pain relief tablets is vital for effectively managing pain and enhancing one’s overall well-being. Each category of pain relief medication—such as acetaminophen, NSAIDs, COX-2 inhibitors, opioids, adjuvants, and corticosteroids—offers unique benefits tailored to specific pain types and conditions. By knowing how these medications work, individuals can choose the most appropriate option for their needs while being mindful of potential side effects and risks.
When searching for effective solutions, many people turn to the best pain relief tablets in India, which provide a variety of options for both acute and chronic pain relief. Consulting healthcare professionals can help ensure that the selected medications are safe and effective for individual circumstances. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of pain relief tablets empowers individuals to take control of their pain management journey, leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
Read More:
10 Home Remedies for Quick Relief from Sore Throat Infection