Introduction
The plasticizers market outlook refers to the anticipated trends, growth drivers, challenges, and opportunities shaping the global plasticizers industry. Plasticizers are chemical compounds added to plastics, particularly polymers like polyvinyl chloride (PVC), to enhance their flexibility, workability, and durability. Widely used across industries like construction, automotive, packaging, and consumer goods, plasticizers play a crucial role in modifying the physical properties of plastics, making them suitable for a range of applications. As the demand for flexible, durable, and high-performance materials increases globally, the plasticizers market is poised for continued growth, driven by various technological, regulatory, and economic factors.
What are Plasticizers?
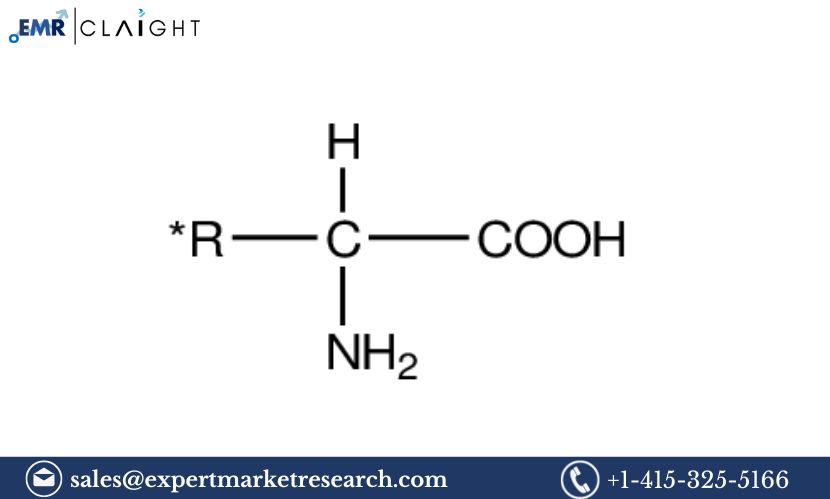
Plasticizers are additives used in polymer formulations to improve their flexibility, elasticity, and workability. They lower the glass transition temperature (Tg) of a polymer, making it more pliable and easier to process. Common types of plasticizers include:
- Phthalates: The most commonly used plasticizers, especially in PVC products, such as flooring, electrical cables, and medical devices.
- Non-phthalates: These are alternative plasticizers that have gained popularity due to health concerns regarding phthalates. Non-phthalates include adipates, citrates, and terephthalates.
- Bio-based Plasticizers: These are derived from renewable sources, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional plasticizers. They are gaining attention due to increasing environmental concerns.
Plasticizers are typically used in manufacturing flexible PVC, and they are added in large quantities to ensure the required level of softness, flexibility, and durability in end products.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/industry-statistics/plasticizers-market/requestsample
Market Overview
The plasticizers market has experienced significant growth over the last few decades, primarily driven by the increasing demand for flexible and durable plastics. With a wide range of applications in industries such as automotive, construction, packaging, and consumer goods, plasticizers are essential for creating products that require flexibility, durability, and performance under varying conditions.
The plasticizers market is influenced by several factors, including raw material costs, technological advancements in plasticizer production, regulatory changes, and shifts in consumer preferences for more sustainable and eco-friendly solutions.
Key Applications of Plasticizers
- Construction: The construction industry is one of the largest consumers of plasticizers, particularly for products like flexible pipes, flooring, roofing materials, and cables. Plasticizers help improve the flexibility and durability of these materials, making them more suitable for residential and commercial buildings.
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, plasticizers are used in automotive interior components such as dashboard coverings, seat covers, and trim elements. They enhance the durability and flexibility of materials that are subjected to varying temperatures and stress.
- Packaging: Plasticizers are used in packaging materials like films, bags, and containers to improve their flexibility, ease of processing, and overall durability. Flexible packaging, which often contains plasticized PVC, is gaining popularity due to its lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and convenience.
- Consumer Goods: Household products such as flooring, toys, and furniture often contain plasticizers to enhance their softness and flexibility. Additionally, plasticizers are used in medical devices like tubing, bags, and catheters due to their ability to make materials more pliable and comfortable.
- Agriculture: Plasticizers are also used in the production of agricultural films, which help enhance the quality and yield of crops. These films are commonly used in greenhouses and for soil covering, where flexibility and UV resistance are critical.
Market Drivers
The global plasticizers market is driven by several key factors:
1. Growth of the Construction Industry
One of the primary drivers for the plasticizers market is the rapid growth of the construction industry, particularly in emerging economies. As urbanization increases, there is a rising demand for flexible construction materials such as piping, flooring, and insulation. Plasticizers play a vital role in improving the flexibility and durability of these materials, thus driving the growth of the market.
2. Demand for Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging is an area of significant growth in the plasticizers market. The shift towards lightweight, cost-effective, and convenient packaging solutions has contributed to the increased adoption of plasticizers, particularly in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and consumer goods sectors. Flexible packaging is easy to handle, cost-effective to produce, and offers protection against contamination, moisture, and light, making it an attractive choice for manufacturers.
3. Advancements in Automotive and Consumer Goods
The automotive sector’s increasing demand for lightweight, durable, and high-performance materials is another key factor driving the plasticizers market. In the automotive industry, plasticizers are used in interior components, cables, and wiring, helping to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency while enhancing the overall performance of the vehicle. Similarly, the demand for soft and flexible consumer goods, including furniture, flooring, and clothing, is boosting the plasticizers market.
4. Environmental Awareness and Sustainable Solutions
Growing environmental concerns have led to increased demand for bio-based and non-phthalate plasticizers. These alternatives offer eco-friendly solutions, aligning with consumer and regulatory demands for greener products. Bio-based plasticizers, which are derived from renewable resources such as vegetable oils and plant-based materials, are gaining traction in industries that require non-toxic, biodegradable solutions.
5. Technological Innovations
Technological innovations in the manufacturing process of plasticizers, as well as the development of new and more efficient compounds, are positively impacting the market. For example, the production of high-performance plasticizers has improved, allowing for the creation of more durable, lightweight, and environmentally friendly products. Furthermore, improvements in the production of PVC, the primary material in which plasticizers are used, also contribute to the overall growth of the market.
Global Supply and Demand Outlook
The demand for plasticizers is primarily concentrated in regions like Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, with Asia-Pacific being the largest consumer and producer of plasticizers. The demand for plasticizers is directly related to the growth of key end-user industries such as construction, automotive, packaging, and consumer goods, all of which are witnessing substantial growth, particularly in emerging economies.
1. Supply Chain Dynamics
The supply of plasticizers is largely dependent on the availability of raw materials, particularly phthalates and bio-based derivatives. The production capacity of plasticizers is closely tied to the global petrochemical industry, as many plasticizers are derived from petroleum-based feedstocks. Any disruptions in the supply of these raw materials, such as fluctuations in oil prices or changes in regulatory policies, can impact the global supply chain.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing alternative, sustainable plasticizers made from renewable resources. This shift is not only driven by the environmental benefits of bio-based solutions but also by increasingly stringent regulations surrounding the use of traditional phthalate-based plasticizers, particularly in products intended for children or medical applications.
2. Demand Outlook in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, are expected to witness substantial growth in the demand for plasticizers due to the rapid industrialization and urbanization occurring in these regions. As infrastructure development, housing projects, and consumer goods manufacturing expand, the demand for plasticizers in sectors such as construction, packaging, and automotive will continue to rise.
In addition, increasing awareness of the benefits of bio-based and non-phthalate plasticizers in these regions is likely to drive the demand for these products, as consumers and regulators push for safer and more sustainable options.
Key Market Players
Several key players dominate the global plasticizers market, offering a wide range of products across different regions and industries. These players are focused on product innovation, geographical expansion, and sustainability efforts to maintain their competitive edge.
1. BASF SE
BASF SE is one of the leading manufacturers of plasticizers, offering a wide range of products for industries such as construction, automotive, and packaging. The company’s strong focus on sustainability and product innovation has helped it maintain a leading position in the market.
2. Eastman Chemical Company
Eastman Chemical is a major producer of both traditional and bio-based plasticizers. The company is known for its wide range of high-performance plasticizers and has made significant strides in developing sustainable solutions for its customers.
3. ExxonMobil Chemical
ExxonMobil Chemical is a prominent player in the global plasticizers market, supplying a broad portfolio of plasticizers used in various applications, including automotive, packaging, and construction. The company is dedicated to innovation and sustainability.
4. Lanxess AG
Lanxess AG, a global specialty chemicals company, offers an extensive range of plasticizers, including alternatives to traditional phthalate-based products. The company focuses on developing environmentally friendly and safe plasticizer solutions.
5. Evonik Industries AG
Evonik Industries is another leading player in the plasticizers market, providing advanced solutions for various applications, including medical devices, packaging, and automotive. The company is committed to sustainable product development and eco-friendly alternatives to conventional plasticizers.
FAQ
1. What are plasticizers used for?
Plasticizers are added to plastics, particularly PVC, to enhance their flexibility, durability, and workability. They are used in construction, automotive, packaging, and consumer goods.
2. What are the main types of plasticizers?
The main types of plasticizers include phthalates, non-phthalates, and bio-based plasticizers. Non-phthalates and bio-based plasticizers are gaining popularity due to health and environmental concerns.
3. How does environmental concern affect the plasticizers market?
There is a growing demand for eco-friendly plasticizers, such as bio-based and non-phthalate options, driven by regulatory pressures and consumer preferences for sustainable products.
4. Who are the key players in the plasticizers market?
Key players in the plasticizers market include BASF SE, Eastman Chemical Company, ExxonMobil Chemical, Lanxess AG, and Evonik Industries AG.
5. What are the growth prospects for the plasticizers market?
The plasticizers market is expected to grow steadily due to increasing demand from the construction, automotive, packaging, and consumer goods industries, as well as innovations in bio-based and non-phthalate plasticizers.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au